

Compounding involves the preparation of customised medications by altering, combining, or formulating active and inactive ingredients to meet specific patient needs following a prescriber's directions (Carvalho and Almeida, 2022). Personalised treatments are made with pharmaceutical active ingredients; therefore, all the compounded treatments are prescription only medications.
This process involves collaboration between patients, healthcare professionals, prescribers and compounding pharmacists, to develop treatments that address the specific dermatological needs of each patient, offering a better patient care (Reeves et al, 2017). This personalised strategy aims to improve the effectiveness, tolerance, and adherence to specialised dermatological therapies.
This introduction explores the foundational aspects of dermatological compounding, tracing its historical evolution and the scientific underpinnings that define this cutting-edge treatment modality.
Historical development and modern applications
The history of compounding in dermatology is rich and varied, tracing back to ancient times (Helm et al, 2017). The art of preparing customised topical formulations has undergone significant transformations. Today, advancements in personalised testing and science have elevated dermatological compounding to a premier position in the world of specialised skincare.
Benefits of compounding in dermatology
Through compounding preparations, healthcare providers can formulate customised topical preparations to address the specific concerns and skin conditions of their patients.
Compounding personalised skincare offers the capability to modify the potency, delivery mechanism, and specific active components of a formulation, as well as the removal of allergens. This adaptability permits clinicians to refine treatments, ensuring maximum efficacy while minimising the risk of adverse effects (Oliveira and Almeida, 2023). Patients derive significant benefits from having their unique needs addressed, as this approach empowers patients to actively participate in their treatments, leading to improved adherence and superior overall outcomes.
The use of compounding skincare involves a patient-prescriber-pharmacist triad to ensure that patients receive tailored, safe, and effective treatments, while fostering collaboration among healthcare professionals.
Compounding also plays a pivotal role in providing access to unique, hard-to-find active ingredients that may not be readily available in mass-produced pharmaceutical products. This capability enables healthcare providers to explore alternative treatments for individualised skincare solutions.
In conclusion, the integration of pharmaceutical compounding and dermatology plays a key role in the treatment of skin conditions promoting a new era of individualised skincare solutions that cater to the unique needs of each patient. This innovative skincare approach not only enhances treatment efficacy but also improves patient satisfaction and long-term skin health outcomes.
These bespoke formulations offer a multitude of benefits, significantly enhancing treatment efficacy and patient satisfaction.
Regulatory framework for compounded skincare in the UK
In the United Kingdom, the regulatory framework for compounded skincare products guarantees the safety and efficacy of these bespoke formulations. The UK's stringent regulation and safety standards dictate the compounding method, labelling, and distribution of compounded pharmaceuticals, including those utilised in dermatological treatments.
Safety standards and quality control
Compounded skincare products in the UK are mandated to conform to rigorous safety standards and quality control protocols. Pharmaceutical compounding facilities are compelled to adhere to General Pharmaceutical Council's standards, thereby ensuring consistent product quality and purity. Regular inspections and testing are imperative to verify that compounded preparations adhere to established pharmaceutical standards.
Compounding pharmacies are obligated to meet exhaustive professional guidelines stipulated by regulatory entities such as the General Pharmaceutical Council (GPhC) and the Royal Pharmaceutical Society (RPS).
| Benefits of customised topical preparations | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced treatment efficacy and compliance |
|
| Improved patient satisfaction |
|

By adhering to the UK's comprehensive regulatory framework, healthcare providers can confidently prescribe their patients customised compounded skincare solutions that represent the highest level of quality and safety.
The role of compounding in modern dermatology practice
This degree of personalisation is particularly beneficial in scenarios where standard commercial formulations fall short or are unsuitable, such as in the management of persistent skin disorders, addressing treatment-resistant conditions, or managing intricate combinations of symptoms.
Meeting individual patient needs
By harnessing the capabilities of compounding, dermatology practices can deliver a bespoke, all-encompassing approach to skin health, resulting in superior outcomes and enhancing the overall quality of care for their patients.
Essential components of compounded skincare formulations
In compounding the selection and combination of ingredients are paramount for addressing specific dermatological conditions. This segment explores the fundamental components that comprise these bespoke skincare formulations, highlighting the science and expertise needed for their creation.
Compounded skincare products are made to tackle a broad spectrum of dermatological conditions, both chronic and acute skin. The ingredients used in these formulations are meticulously selected, based on their demonstrated efficacy, synergy and safety assessments.
Compounding pharmacists collaborate closely with prescribers to create bespoke formulations that address the unique attributes and condition of each individual's skin.
Professional integration in aesthetic practice
In the world of aesthetic nursing, the incorporation of compounded medical skincare solutions into treatment plans marks a significant change in patient care. This shift is driven by understanding why and how to seamlessly integrate compounding into their aesthetic practice. Such integration not only enhances patient experiences but also gives remarkable results, thereby elevating the standard of care.
The rationale behind aesthetic nurses' consideration of compounding is multifaceted. Firstly, customised formulations enable targeted treatment of specific skin concerns, addressing the unique needs of each patient. Secondly, compounded products are tailored to individual preferences and sensitivities, thereby improving treatment efficacy by enhancing patient compliance.
The integration of compounding in aesthetic practice empowers aesthetic nurses to deliver personalised care and helps to distinguish their practice. This not only optimises treatment outcomes but also strengthens patient-provider relationships, leading to increased patient satisfaction and loyalty.
| Common compounding ingredients | Targeted dermatological conditions |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Steps to follow to successfully integrate personalised skincare:
1) Obtain patient consent and medical information
2) Assess patient's unique skincare needs and goals
» The art of customised topical formulations has undergone significant transformations. Today, advancements in personalised testing and science have elevated dermatological compounding to a premier position in the world of specialised skincare «
3) Collaborate with a trusted compounding pharmacy to design tailored formulations
Work closely with a reputable compounding pharmacy to create customised skincare formulations. At Roseway Labs we use high-quality, pharmaceutical-grade ingredients to ensure the formulations are safe, effective, and suited to the patient's specific needs and treatment goals. This collaboration ensures that the compounded products meet the patient's unique skin profile while upholding the highest standards of quality.
4) Incorporate compounded products into the patient's comprehensive treatment plan
5) Monitor and adjust treatment protocols
| Assessment method | Objective | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Skin examination | Evaluate condition's response to compounded formulation | Provides direct visual assessment of treatment progress |
| Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) | Gauge patient's perception of treatment effectiveness | Incorporates patient's subjective experience and satisfaction |
| Objective measurements | Track quantifiable changes in condition, such as lesion size or hydration levels | Offers data-driven insights to guide treatment adjustments |
| Photographic documentation | Visually monitor the progression of the dermatological condition | Provides a visual record to compare treatment outcomes over time |
Progress assessment methods
Assessing a patient's progress is a critical step in providing high-quality compounded skincare treatments.
Healthcare providers employ a variety of assessment methods, including:
Treatment modification strategies
Healthcare professionals, armed with insights from progress assessments, can then make informed decisions about modifying the treatment protocol.
This may involve:
By continuously monitoring the patient's progress and adapting the treatment plan accordingly, healthcare providers can ensure that the individualised compounded skincare solutions remain effective and tailored to the patient's unique dermatological conditions.
6) Provide patient education and compliance strategies
The success of customised topical preparations in dermatological treatments hinges on patient compliance. It is imperative to equip patients with the requisite knowledge and tools to achieve optimal results. This section delves into effective patient education strategies and the promotion of adherence to prescribed aftercare regimens.
Educate patients on proper application techniques
Clear, concise instructions on the correct application of customised topical preparations are key. Patients must grasp the correct dosage, application frequency, and the necessity to avoid sensitive areas such as the eyes or mucous membranes. Demonstrating the application technique can significantly enhance patient comprehension and adherence.
Emphasise the significance of adherence
It is crucial for patients to understand the significance of adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen. Educate them on the potential consequences of non-compliance, including reduced efficacy or adverse reactions. Encourage open dialogue, enabling patients to express any concerns or challenges they encounter in adhering to the treatment plan.
By empowering patients with the necessary knowledge and support, healthcare professionals can foster a collaborative partnership further helping to enhance treatment adherence and improve patient outcomes.
7) Use documentation and follow-up protocols
The meticulous recording of compounded skincare treatments and adherence to follow-up protocols are indispensable. Such practices are not merely regulatory compliance but are key in ensuring patient safety and maximising treatment efficacy. They underscore the importance of maintaining detailed records, which are fundamental to the practice of compounded dermatological solutions in the UK.
In the step of patient evaluation and consent, healthcare professionals must document every aspect of the process with precision. This includes the patient's medical history, a comprehensive skin assessment, and any pertinent laboratory tests. The acquisition of informed consent from the patient is a critical step, necessitating thorough documentation of the discussion and the patient's consent.
Accurate records of the compounded formulation, its constituents, and the dispensing process are imperative for upholding UK regulation and safety standards. These records act as a valuable resource for healthcare providers, facilitating traceability and quality control of the customised treatments.
Regular follow-up appointments are equally crucial, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor patient progress, assess treatment efficacy, and make any necessary adjustments to the formulation or dosage. It is essential to document the patient's response, any adverse reactions, and the rationale behind any modifications. This ensures the continued safety and efficacy of the compounded skincare treatment.
By adhering to comprehensive documentation and follow-up protocols, healthcare providers not only ensure patient evaluation and consent but also demonstrate their unwavering commitment to UK regulation and safety standards. This diligent approach fosters trust, optimises patient outcomes, and maintains the highest standards of professionalism in the practice of compounded dermatological solutions.
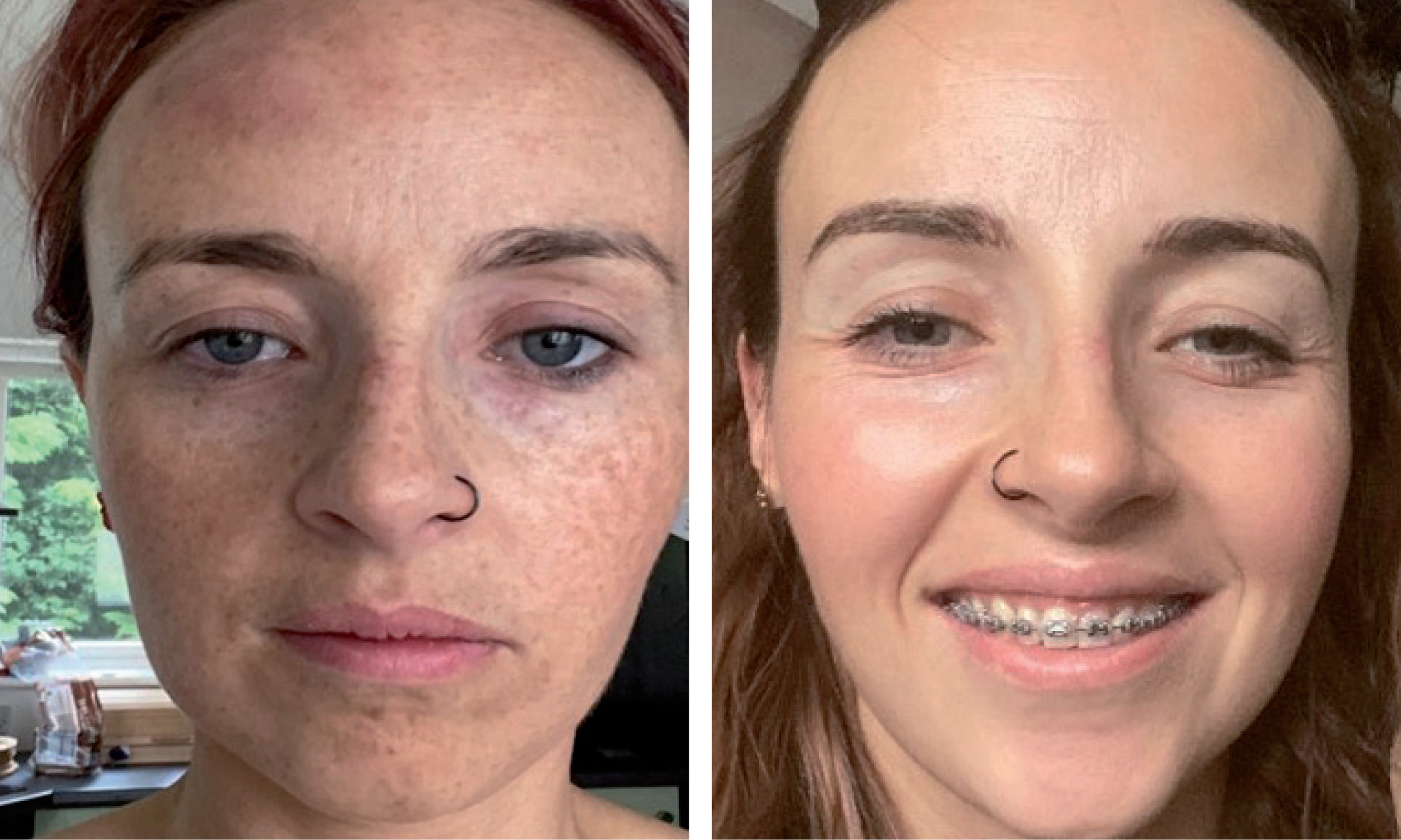
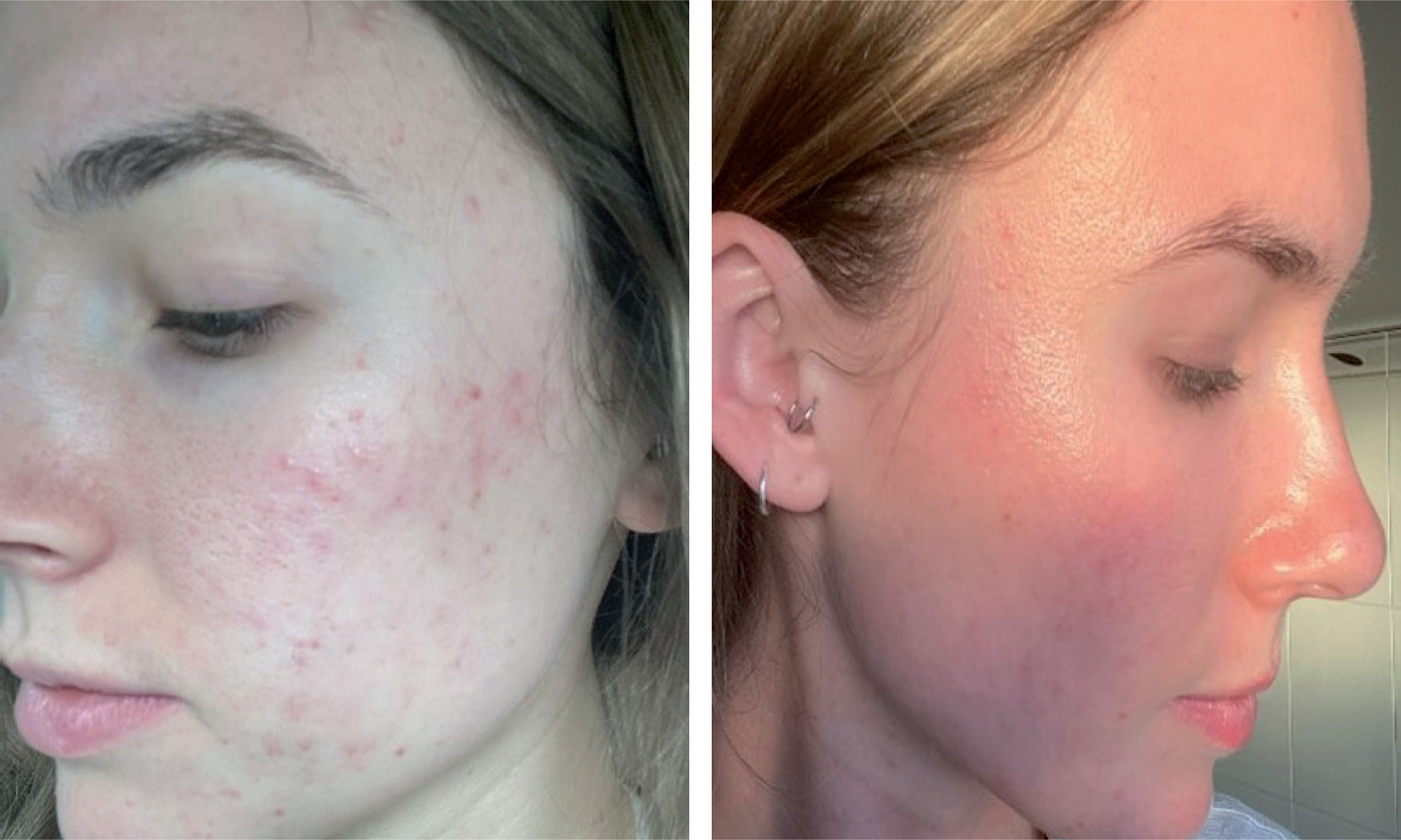
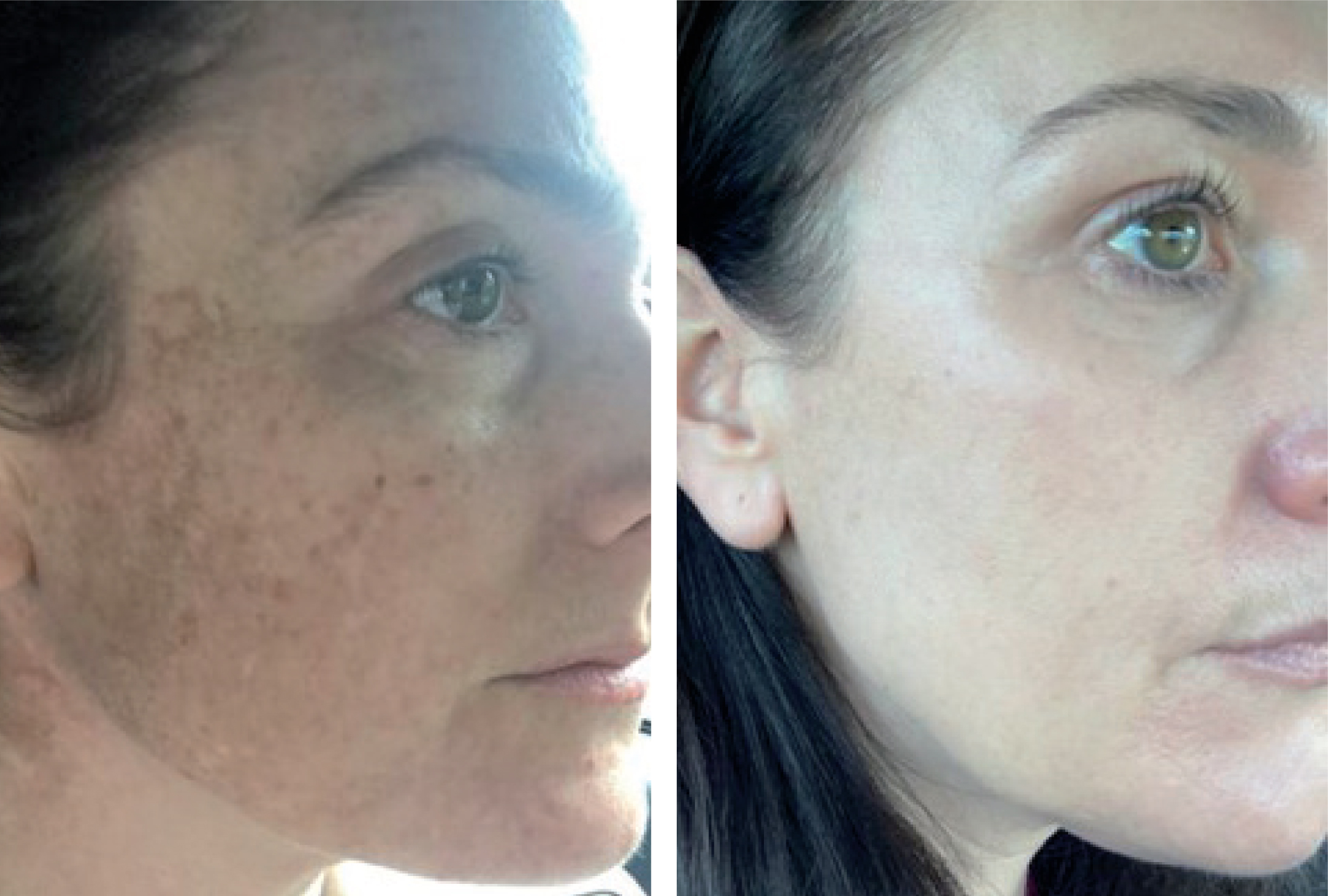
Case studies
See images A-H for case study images.
Conclusion
The rise of compounding in dermatology highlights the growing need for personalised skincare solutions in aesthetic treatments. This overview explains the science behind dermatological compounding and how it's helping treat a wide range of skin conditions.
With compounded skincare, healthcare professionals and aesthetic nurses can create custom treatments that are specifically designed for each person's unique needs. This makes treatments more effective and increases the chances that patients will adhere to their skincare routines. By combining compounded skincare with aesthetic treatments practitioners can offer more personalised care, improving both results and patient satisfaction.


As regulations and quality standards continue to improve, the future of personalised skincare looks even brighter. Both practitioners and patients are excited about a new era in dermatology, where customised skincare will become the norm, transforming how we treat and understand skin conditions and unlocking the full potential of topical treatments.



