

One of the areas where AI shines in dermatology is skin cancer detection. AI algorithms can analyse images of skin lesions and classify them as benign or malignant, providing dermatologists with crucial information for early intervention. By enabling early detection, AI can significantwly increase the chances of successful treatment, potentially saving lives.
Furthermore, AI can optimise treatment plans by analysing comprehensive patient data, including medical history, genetics and treatment outcomes. By identifying patterns and predicting response to therapies, AI algorithms can assist dermatologists in determining the most effective interventions for each patient. To further note, ultrasound coupled with AI offers the potential to optimise treatment efficacy through precise tissue targeting, improving real-time image analysis, treatment planning, and personalised outcome prediction in aesthetics.
In addition, AI facilitates remote consultations through teledermatology, where patients can capture images of their skin conditions, which are then analysed by AI algorithms. Dermatologists can review the insights provided by AI to make accurate diagnoses and provide treatment recommendations remotely. This enables increased access to dermatological expertise, especially in underserved areas and rural communities.
Moreover, AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots play a valuable role in healthcare by providing basic healthcare information, answering medical queries, and assisting in triaging patients and scheduling appointments.
Additionally, AI streamlines administrative tasks such as medical coding, billing and scheduling, reducing the burden on healthcare professionals. While the application of AI in dermatology is promising, it is important to recognise that it should be seen as a supportive tool rather than a replacement for dermatologists. Human expertise, clinical judgment, and the patient-doctor relationship remain integral to quality care.
Dermatologists can use AI-generated insights as valuable guidance in their decision-making processes, enhancing their ability to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.
Furthermore, incorporating the stakeholder taxonomy into the decision framework for AI implementation in dermatology ensures a comprehensive approach. Patients' experiences and wellbeing are prioritised through patient-centered principles, while healthcare providers' feedback ensures user-friendly AI tools. Payers' considerations address costs and resource allocation. Regulatory authorities ensure compliance with relevant laws and ethical guidelines. Technology vendors contribute their expertise, and collaboration with research institutions fosters innovation and validation. Legal and ethical experts address potential dilemmas.
By considering the perspectives and needs of all stakeholders, the decision framework ensures responsible and successful integration of AI in dermatology, benefiting patients, providers, payers, and society at large. The suitability of supervised machine learning depends on meaningful correlations between measured variables and outcomes. Its applicability and value in the real-world, on the other hand, hinges upon its enhanced performance based on well-annotated data which in turn provides the possibility of an intervention founded by positive predictive values of the model used to identify a certain population. In conclusion, AI has the potential to revolutionise dermatological care by improving diagnostics, treatment decisions, and patient outcomes. Its ability to analyse images, optimise treatment plans, and facilitate remote consultations can significantly benefit patients, particularly in areas with limited access to dermatological expertise. By embracing AI in dermatology, we can enhance the delivery of quality care and make significant strides in combating skin diseases.
Overview
In recent years, the field of artificial intelligence (AI) has seen rapid advancement and is increasingly becoming a cornerstone in the evolution of healthcare (Holzinger et al. 2019). AI, particularly through machine learning and deep learning algorithms, has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in processing and interpreting complex data sets, identifying patterns that may not be immediately evident to human observers, and learning from each interaction to improve future performance (Herman, 2022; Huynh-The et al, 2022). In healthcare, AI applications range from predictive analytics and patient triage to personalised medicine and advanced diagnostics (Schielein et al, 2023). The integration of AI into dermatology is a burgeoning area of interest, with the potential to revolutionise how skin conditions are diagnosed and treated. AI algorithms, particularly those trained on large datasets of dermatological images, can assist in identifying subtle nuances in skin lesions that may elude even the most seasoned of dermatologists. This is especially significant in the early detection of skin cancer, where AI's ability to scrutinise images for irregularities can expedite diagnosis and intervention, potentially saving lives (Haykal et al, 2023; Esteva et al, 2017).

Comparing the diagnostic accuracy of AI with traditional dermatological methods reveals a compelling narrative. Traditional diagnostic practices are heavily reliant on the dermatologist's expertise, derived from years of study and patient interactions. These methods, while effective, can sometimes lead to variability in diagnosis due to human error or oversight (Babaei et al, 2023). AI, on the other hand, offers a level of consistency and precision that can supplement the dermatologist's skillset. Research has indicated that AI systems, when properly trained, can achieve diagnostic accuracies that are comparable to or even surpass those of human experts, particularly in the detection of melanoma and other skin cancers (Gutkowicz-Krusin et al, 2000; Jumper et al, 2021; Li et al, 2022). The synergy between AI and traditional dermatological practices offers a promising pathway towards more accurate diagnoses, improved treatment outcomes, and enhanced patient care. As AI technology continues to evolve and integrate more deeply into the healthcare system, it is poised to complement the expertise of dermatologists, rather than replace it, fostering a new era of innovation in dermatological care (Muralidharan et al, 2023).
However, the integration of AI into dermatology does not come without challenges (Cohen et al, 2020). Issues such as algorithm bias, data privacy, and the need for extensive validation before clinical deployment are significant hurdles (Cohen et al, 2020). Moreover, the human aspect of patient care as understanding patients' concerns, providing reassurance, and tailoring treatments to individual needs remains irreplaceably within the domain of the dermatologist.
The transformative potential of ai in dermatology
The integration of AI into healthcare, especially dermatology, marks a significant shift towards precision medicine, offering substantial improvements in the early detection of skin cancer and other skin-related conditions. This technological advancement enables dermatologists to achieve higher diagnostic accuracy, customise treatment strategies to each patient's specific needs, and extend healthcare accessibility through teledermatology and AI-enhanced remote consultations (Elder et al, 2021). As AI becomes more embedded in clinical workflows, its potential to revolutionise patient care, enhance diagnostic processes, and streamline administrative tasks grows exponentially (Ting et al, 2020). This evolution in healthcare technology not only boosts the efficiency and effectiveness of dermatologists but also significantly betters patient care outcomes by enabling quicker, more accurate diagnoses and treatments tailored to the individual's unique health profile (Kulkarni and Singh, 2023). In a nutshell, the integration of AI into dermatology offers a promising path toward enhancing the early detection of skin cancers, enabling personalised treatment plans, and facilitating AI-driven remote consultations. As these technologies continue to evolve and mature, they hold the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes, streamline healthcare delivery, and democratise access to specialised dermatological care (Takiddin et al, 2021).

Benefits to healthcare professionals and patient care
AI is redefining the realm of dermatology, offering unprecedented advancements in patient care and operational efficiency. From elevating diagnostic accuracy to optimising patient engagement and streamlining healthcare workflows, AI's integration into dermatology is setting new standards for personalised and efficient patient care (Flament et al, 2021; Flament et al, 2022).
Enhanced diagnostic accuracy
AI aids in reducing diagnostic errors, ensuring patients receive correct and timely treatments. By supporting dermatologists with image analysis and pattern recognition, AI enhances diagnostic precision (Flament et al, 2023).
Improved patient experience
The use of AI-driven tools for patient education, triage, and personalised communication fosters a more engaged and informed patient population. It ensures patients are promptly seen based on their needs, enhancing overall satisfaction and care outcomes (Gherghina et al, 2018).
Access to cutting-edge treatments and research
AI algorithms are capable of processing vast amounts of data from clinical studies, patient records, and the latest dermatological research at an unprecedented speed. This enables healthcare professionals to stay abreast of the latest treatment options and diagnostic techniques, potentially introducing innovative treatments to patients much quicker. Additionally, AI's data analysis capabilities can identify patterns and treatment outcomes that may lead to novel dermatological insights and advancements, further enhancing patient care quality (Li et al, 2022; Li et al, 2020).
Streamlined workflow and increased efficiency
AI can automate routine tasks such as appointment scheduling, patient data management, and preliminary analyses of patient symptoms and images. This frees up healthcare professionals to focus more on direct patient care rather than administrative duties, leading to more efficient use of time and resources (Zayas-Cabán et al, 2021).

How do AI algorithms analyse patient data to tailor treatment approaches?
AI's role extends beyond diagnosis into the development of personalised treatment plans. In dermatology, AI algorithms revolutionise patient care by integrating and analysing diverse data types, such as medical histories, genetic markers and dermatological images through sophisticated pattern recognition and predictive analytics. This process enables the identification of nuanced disease patterns and the prediction of disease progression and treatment responses. By leveraging these insights, AI tailors highly personalised treatment plans, considering the unique genetic, lifestyle, and health profiles of each patient, potentially improving outcomes and minimising side effects. For instance, AI can help predict how a patient might respond to a particular medication based on similar patient profiles, thereby optimising the treatment regimen to achieve the best possible outcome (Schork, 2019).
The critical role of transparent, relevant and trustworthy datasets
The foundation of effective AI lies in the quality of its datasets. Transparent, relevant and trustworthy datasets are pivotal for developing AI systems that are not only efficient but also fair and ethical.
Together, these qualities help mitigate the risks of biased outcomes, promote fairness, and foster trust among users, which are all essential for the wide-scale adoption and success of AI technologies (Haykal et al, 2023; Daneshjou and Kittler, 2023).
AI-driven remote consultations and teledermatology
The integration of AI into remote consultations has revolutionised various aspects of healthcare, making dermatological care more accessible to patients, regardless of their geographic location, offering a unique blend of efficiency, accuracy and personalised care. AI-driven platforms can triage skin lesions in photographs submitted by patients, identifying cases that warrant further examination by a dermatologist. This streamlines the consultation process and ensures that patients with urgent conditions are prioritised. Moreover, AI can support dermatologists during virtual consultations by providing real-time diagnostic suggestions and treatment options, enhancing the quality of care delivered remotely (Ting et al, 2020).
Moreover, AI-driven analysis provides dermatologists with pre-diagnosis insights, making remote consultations more focused and productive. This blend of AI and telehealth technology is particularly beneficial in areas with limited access to dermatological services. Several studies reported that AI-assisted teledermatology led to a significant improvement in diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy, underscoring the technology's potential to bridge the gap in dermatological care (Shapiro et al, 2024; Tognetti et al, 2021; Cazzaniga et al, 2019).
AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots in dermatology
AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots are transforming the landscape of dermatology, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of patient care through advanced diagnostics, improved patient engagement, and continuous education and follow-up. By leveraging the power of AI, these tools are supporting dermatologists in accurately diagnosing skin conditions and revolutionising the way patients interact with healthcare providers, access information, and manage their treatment plans. Exploring further, these AI technologies act as key players in revolutionising dermatological practice, not just by augmenting diagnostic precision but also by streamlining patient communication and care management, marking a new era in the way skin health is approached and treated (Marks and Haupt, 2023).
» AI algorithms have shown remarkable proficiency in analysing dermatological images with impressive accuracy, such as skin lesions, rashes and moles «
Diagnostic support
AI-driven virtual assistants and chatbots in dermatology make diagnostic support possible through advanced image analysis and machine learning algorithms. These technologies are trained on vast datasets of dermatological images, enabling them to recognise patterns, anomalies, and signs of skin conditions with a high level of accuracy.
When a patient uploads an image of a skin concern via a virtual platform, the AI analyses it in real-time, identifying potential conditions by comparing it against its extensive database. This immediate feedback can help patients by providing a preliminary assessment (Draelos and Draelos, 2011).
Patient engagement and triage
Virtual assistants and chatbots are at the forefront of patient interaction, guiding patients through symptom checking, providing information on common skin conditions, and prioritising cases based on urgency. This pre-consultation triage ensures that patients receive timely attention based on the severity of their condition (Yan et al, 2024).
Education and follow-up
These AI tools also play a critical role in patient education, offering advice on skin care routines, preventive measures and medication management. They can automate follow-up communications, reminding patients of care instructions or when it's time for a check-up, thus enhancing the continuity of care (Palanica et al, 2019).
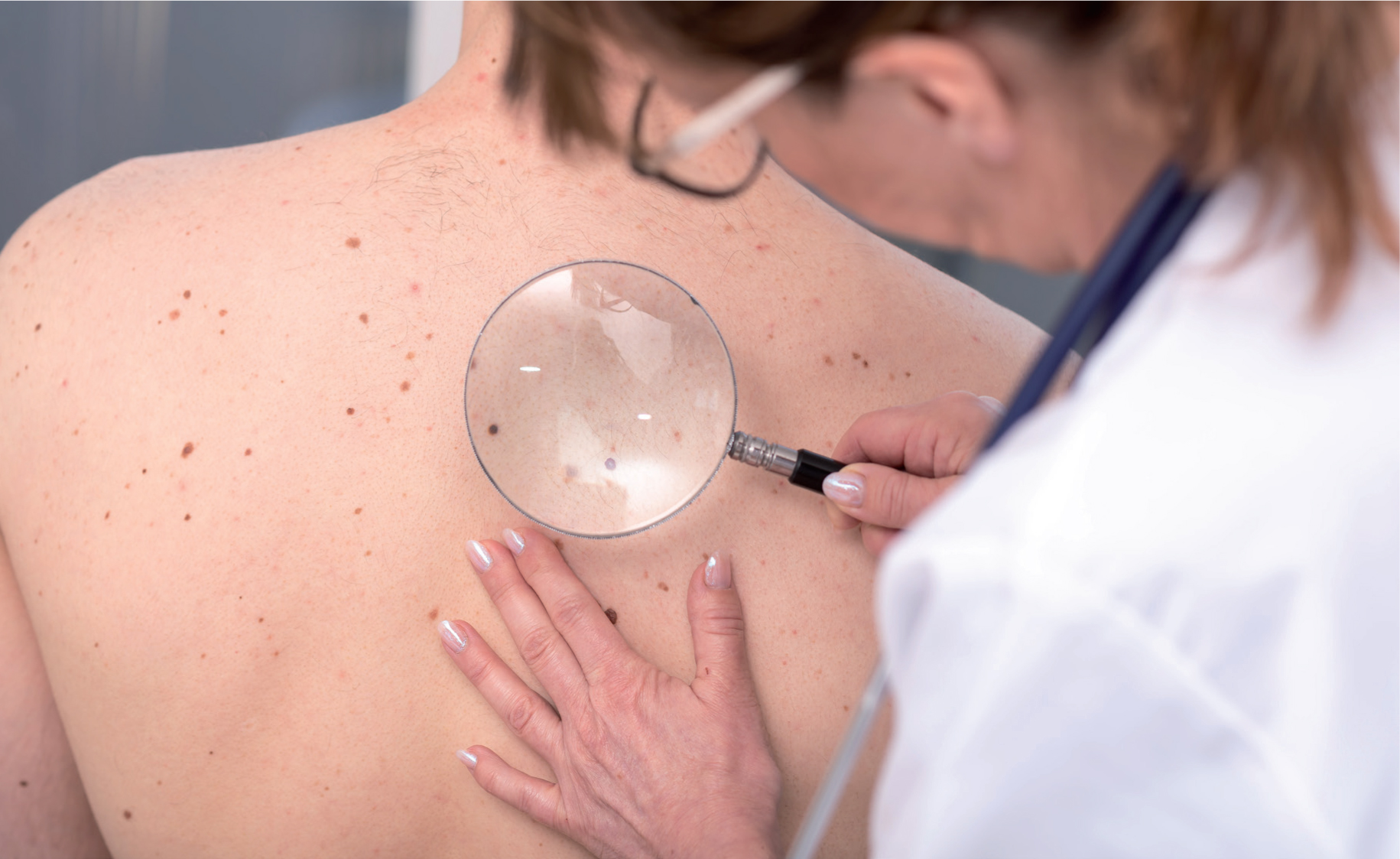

Empowering patients as masters of their skincare
The emergence and public access to face scan applications represent a significant shift in skincare, empowering individuals to take charge of their skin health. These applications utilise advanced AI and machine learning algorithms to analyse images of the skin, providing users with insights about their skin condition, potential concerns, and even tracking changes over time. Their ability to process and analyse data with exceptional speed and accuracy underscores a significant leap forward in both diagnosing skin conditions and enhancing patient engagement. Moreover, the personalised skincare recommendations offered by these applications are tailored to the unique characteristics of the user's skin, considering factors such as skin type, condition, and environmental influences. Consequently, this tailored advice can lead to better skin health outcomes and more efficient and cost-effective skincare routines (Ouellette and Rao, 2022).
Self-diagnosis and early detection
Face scan applications offer the tools for early detection of skin issues. By enabling users to scan their skin regularly, these apps can help in identifying changes or anomalies early on, prompting timely consultation with dermatology professionals (Kaliyadan and Ashique, 2020; Eapen, 2020; Patel et al, 2021).
Personalised skincare recommendations
Leveraging data from skin analyses, these applications can provide personalised skincare advice. This includes recommendations for skincare routines, products best suited for their skin type, and tips for preventing skin damage. Such tailored advice helps individuals optimise their skincare practices, contributing to better skin health (Sunkara et al, 2023).
Augmented reality (AR) apps
These apps are transforming virtual encounters by overlaying digital information onto the real world, enhancing user experiences across various domains. From interactive educational tools that bring lessons to life, to immersive shopping experiences that allow consumers to visualise products in their own space, AR applications bridge the gap between virtual and physical realities. This seamless integration enriches user engagement and opens new avenues for innovation, making AR a pivotal technology in shaping future digital interactions (Sharma et al, 2019; Obagi et al, 2020; Bruno et al, 2022).
Monitoring and tracking
Patients can use these applications to monitor the progress of their skin condition over time. This feature is particularly beneficial for individuals undergoing treatment for skin conditions, as it allows for tracking improvements or identifying the need for adjustments in treatment plans (Chao et al, 2017).
Educational resource
Beyond diagnostic and tracking capabilities, face scan applications serve as an invaluable educational resource. They often provide information on skin health, the impact of lifestyle choices on skin condition, and protective measures against environmental damage (Yan et al, 2024; Kye et al, 2021).
The development and widespread adoption of face scan applications signal a significant advancement in personal healthcare, particularly in the realm of dermatology. These applications leverage cutting-edge AI and machine learning technologies to analyse users' skin conditions through simple photographs taken with smartphones.
This technological leap democratises access to skin health information and fosters a more informed and proactive public when it comes to skin care and treatment. With these tools, individuals are no longer passive recipients of healthcare advice but active participants in their skincare regimen. The ability to quickly scan and receive feedback on one's skin condition encourages a proactive approach to skin health, making early detection of potential issues a part of routine self-care. This is particularly crucial in dermatology, where early detection can significantly impact the outcome of various skin conditions, including skin cancer (Kumar and Sinha, 2023). However, the rise of face scan applications also brings to light the need for careful consideration of privacy and data security. Users are uploading sensitive personal data, and the responsibility is on the developers and companies behind these apps to ensure that this data is protected. It is crucial for these applications to be used as supplements to, rather than substitutes for, professional dermatological care (Kaliyadan and Ashique, 2020).
The role of public access to these applications
The integration of face scan applications into everyday skincare routines exemplifies the broader trend of technology-enabled, patient-centered care. By providing easy access to skin health information and personalised care recommendations, these applications improve individual skin health outcomes and contribute to a more informed and health-conscious society.
As technology continues to evolve, the potential for even more advanced applications and tools to support skin health and other areas of personal wellness is immense, promising a future where individuals are even more empowered to take charge of their health (Gherghina et al, 2018).
Democratisation of skincare
By making advanced skin analysis technology widely accessible, these applications democratise skincare. Individuals, regardless of their location or income level, gain access to tools that were previously available only in clinical settings (Maudet et al, 2023).
Informed consultations
When individuals use these applications as a preliminary step before seeing a professional, they are better informed about their skin condition. This can lead to more productive consultations, as patients are better equipped to describe their concerns and symptoms (Elder et al, 2021).
Encouraging proactive skin health management
The ease of use and accessibility of face scan apps encourage a more proactive approach to skin health. Users are more likely to take early action on skin issues, seek professional advice when necessary, and maintain regular skincare routines (Maudet et al, 2023).


» The integration of AI technologies into dermatological practices has the power to significantly improve diagnostics, treatment decisions, and overall patient outcomes «
Bridging gaps in dermatological care
In regions with limited access to dermatological care, these applications can play a crucial role in bridging the gap. They provide a first line of information and guidance, helping to identify when professional care is necessary (Ting et al. 2020).
Impact of AI on administrative tasks
AI is also revolutionising non-clinical administrative tasks, streamlining operations, and enhancing efficiency across various industries. By automating routine and time-consuming tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, AI frees up human resources to focus on more complex and strategic activities. This boosts productivity and reduces the likelihood of errors associated with manual processes (Sharma et al, 2019; Tam et al, 2023).
Coding and billing
AI applications streamline the coding and billing process by accurately identifying services rendered during a consultation and mapping them to the appropriate codes. This automation reduces errors, ensures compliance with healthcare regulations, and speeds up the reimbursement process (Abdullah et al, 2020).
Scheduling
AI-powered systems can manage appointment scheduling more efficiently by analysing patterns in appointment durations, no-show rates, and patient preferences. These systems can optimise the allocation of resources, reduce waiting times, and improve patient satisfaction (Tam et al, 2023).
Document management and data entry
By automating the transcription of consultation notes and integrating them into electronic health records, AI reduces the administrative burden on healthcare professionals. This allows them to spend more time on patient care and less on paperwork (TerKonda et al, 2024).
Incorporating stakeholder taxonomy in ai implementation
The successful integration of AI in dermatology requires a comprehensive approach that considers the perspectives of all stakeholders involved. This includes prioritising patient-centered care, incorporating feedback from healthcare providers, addressing payers' cost considerations, ensuring regulatory compliance, leveraging technology vendors' expertise, and fostering collaboration with research institutions. By aligning the interests and concerns of these stakeholders, the implementation of AI can be accurate, responsible, and effective (Wiens et al, 2019).
AI: a supportive tool, not a replacement
It is crucial to emphasise that AI serves as a support mechanism in dermatology, augmenting the expertise of dermatologists rather than replacing them. The nuanced understanding, clinical judgment, and empathetic patient care that dermatologists provide are irreplaceable. AI aids in enhancing the accuracy of diagnoses and efficiency of treatment plans, but the final decisions and patient management lie in the hands of human professionals (Kulkarni et al, 2020).
While AI's capabilities in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and facilitating remote consultations are undeniable, it's crucial to recognise that AI serves as a tool to augment, not replace, the expertise of dermatologists. The value of human judgment, experience, and the nuanced understanding of a patient's history and symptoms cannot be replicated by algorithms. While AI can offer valuable insights, it is crucial for the ultimate decision-making responsibility to remain with the experienced professional. This ensures thorough consideration of the intricacies inherent in each case. Moreover, effective dermatological care revolves around the patient-doctor relationship, which hinges on trust, empathy, and communication, qualities that AI cannot emulate (Forsey et al, 2021). By leveraging AI as a supportive tool, dermatologists can enhance their diagnostic and treatment capabilities while preserving the essential human touch of care. This balanced approach ensures that the adoption of AI technology enriches the quality of care provided, without diminishing the irreplaceable value of personal connection in healthcare.
Future directions and challenges
The future could see AI models becoming even more sophisticated, incorporating not just dermatological imaging but also genetic, demographic, and environmental data to predict skin diseases before they manifest visibly (Kumari et al, 2023). Such predictive analytics could revolutionise preventative dermatology, allowing for personalised skincare and treatment regimens that significantly reduce the incidence of severe skin conditions and cancers. Moreover, the integration of AI with emerging technologies like AR and wearable devices presents an exciting frontier. AR can offer dermatologists enhanced visualisation capabilities during examinations and surgeries, while wearable devices equipped with sensors and AI algorithms could continuously monitor skin health, alerting users and healthcare providers to potential issues before they require intensive treatment. Additionally, virtual reality (VR) technology can complement dermatological care by providing immersive educational experiences for both patients and practitioners, facilitating better understanding and collaboration in treatment plans (Obagi et al, 2020; Yu et al, 2018; Georgievskaya, 2022). As we venture deeper into the intersection of AI and dermatology, several promising directions and inherent challenges emerge. These advancements come with their own set of challenges (Gerke et al, 2020). Data privacy and security are paramount concerns, as dermatological data includes highly personal information. Ensuring the ethical use of AI and maintaining patient confidentiality in the age of digital health is a complex issue that requires ongoing attention and robust solutions. Another significant challenge is the issue of bias in AI algorithms. If AI systems are primarily educated using data from specific groups, their effectiveness might diminish for individuals who do not belong to those groups. For instance, if a model is trained with data from older patients in Massachusetts, would it work on younger patients in Paris? This could lead to disparities in care and outcomes, emphasising the need for diverse and representative datasets in training AI models (Hogarty et al, 2020).
However, the regulatory landscape for AI in healthcare is still evolving. Developing standardised guidelines and certifications for AI applications in dermatology will be crucial to ensuring their safety, efficacy and accessibility. As we navigate these challenges, the collaboration between dermatologists, AI researchers, patients, and policymakers will be vital in shaping a future where AI enhances dermatological care without compromising ethical standards or patient trust (Caffery et al, 2023; Sangers et al, 2023).
Conclusion
As AI continues to integrate into dermatological practices, its potential to revolutionise the field becomes increasingly evident. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy and personalising treatment plans to enabling remote consultations and reducing administrative burdens, AI is shaping the future of dermatology. However, its success hinges on careful implementation, consideration of ethical implications, and the preservation of the invaluable dermatologist-patient relationship. By embracing AI as a tool for augmentation rather than replacement, dermatology can harness the full potential of this technology to improve patient outcomes and advance the quality of care. The human element, underscored by the clinical judgment of a healthcare professional and the patient-doctor relationship, remains irreplaceable. By combining the best of AI technology with the invaluable skill, expertise and empathy of human practitioners, we can create a future where dermatological care is more accessible, efficient, and effective than ever before. The journey ahead will undoubtedly present challenges, from ensuring data privacy and overcoming algorithmic bias to navigating the evolving regulatory landscape. Yet, with continued innovation, collaboration, and a commitment to ethical principles, the potential of AI in dermatology can be fully realised. The fusion of technology and human expertise opens a world of possibilities for dermatological care, making what once seemed like science fiction a reality of today's medical practice.



